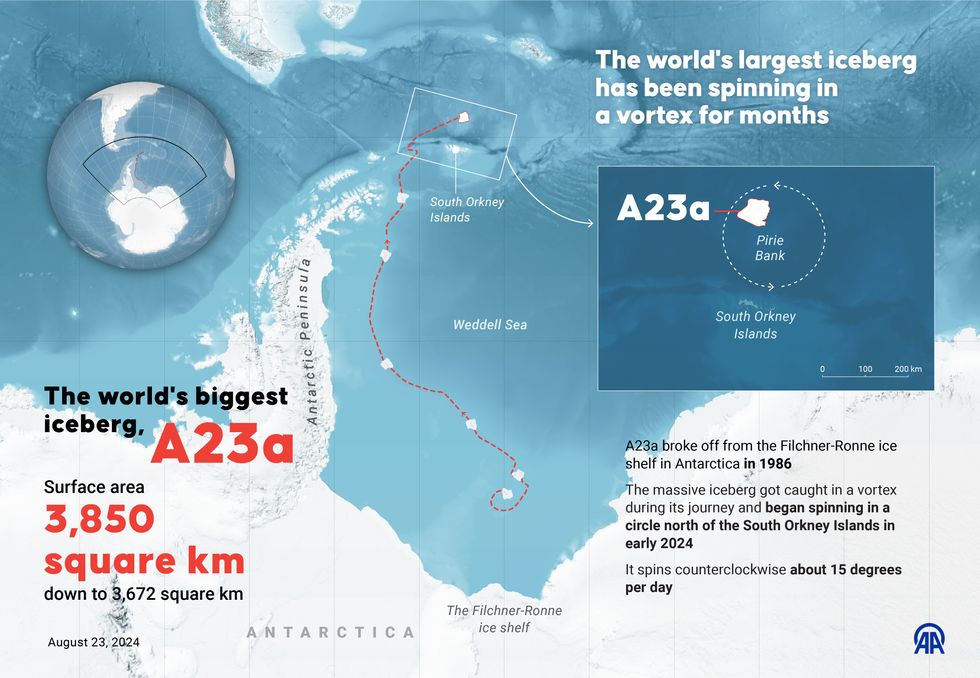
The world's largest and oldest iceberg has finally broken free after being grounded for more than three decades, scientists have confirmed.
A23a - a colossal ice mass weighing nearly a trillion tonnes which weighs twice the size of Greater London - has begun drifting in the Southern Ocean.
The mega-berg, which had recently been spinning in place north of the South Orkney Islands, is now embarking on what experts believe will be its final journey.
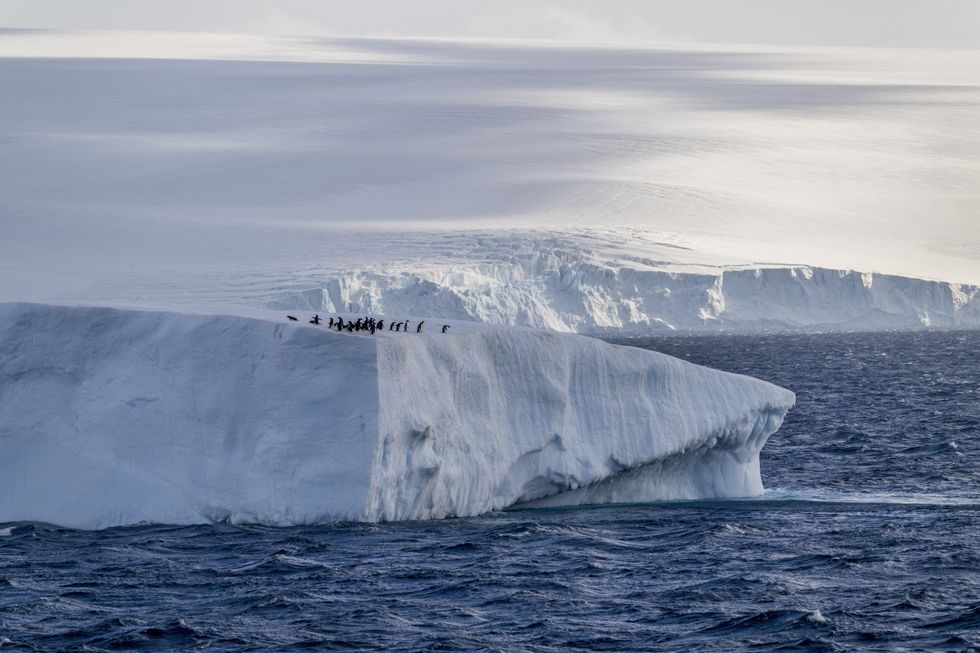
The massive iceberg, measuring about 400 metres in thickness, had been caught in an oceanographic phenomenon known as a Taylor Column.
The massive iceberg, measuring about 400 metres in thickness, had been caught in an oceanographic phenomenon known as a Taylor Column (Stock)
GETTY
After breaking free, A23a remained grounded in the Weddell Sea for over three decades due to its massive underwater structure.
Then, by 2020, the iceberg finally began its slow journey northward, marking the start of its current movement.
Dr Andrew Meijers, an oceanographer with the British Antarctic Survey, expressed enthusiasm about the iceberg's movement, saying: "It's exciting to see A23a on the move again after periods of being stuck," he said.
"We are interested to see if it will take the same route the other large icebergs that have calved off Antarctica have taken," Meijers added.
Scientists have expected A23a to continue its journey into the Southern Ocean, following the powerful Antarctic Circumpolar Current.
A23a is the world's largest iceberg
GETTY
This current is likely to drive the massive iceberg towards the sub-Antarctic island of South Georgia and, as it encounters warmer waters in this region, experts have predicted that A23a will begin to break up into smaller icebergs.
These fragments will eventually melt completely, marking the final chapter in the iceberg's decades-long journey.
Laura Taylor, a biogeochemist on the vessel, explained: "We know that these giant icebergs can provide nutrients to the waters they pass through, creating thriving ecosystems in otherwise less productive areas."
The research team collected water samples from various points around A23a's route to study its environmental effects.
"They should help us determine what life could form around A23a and how it impacts carbon in the ocean and its balance with the atmosphere," Taylor added.

 By GB News (World News) | Created at 2024-12-14 16:41:29 | Updated at 2024-12-14 19:53:44
3 hours ago
By GB News (World News) | Created at 2024-12-14 16:41:29 | Updated at 2024-12-14 19:53:44
3 hours ago