Sign up for our free Health Check email to receive exclusive analysis on the week in health
Get our free Health Check email
Get our free Health Check email
I would like to be emailed about offers, events and updates from The Independent. Read our privacy policy
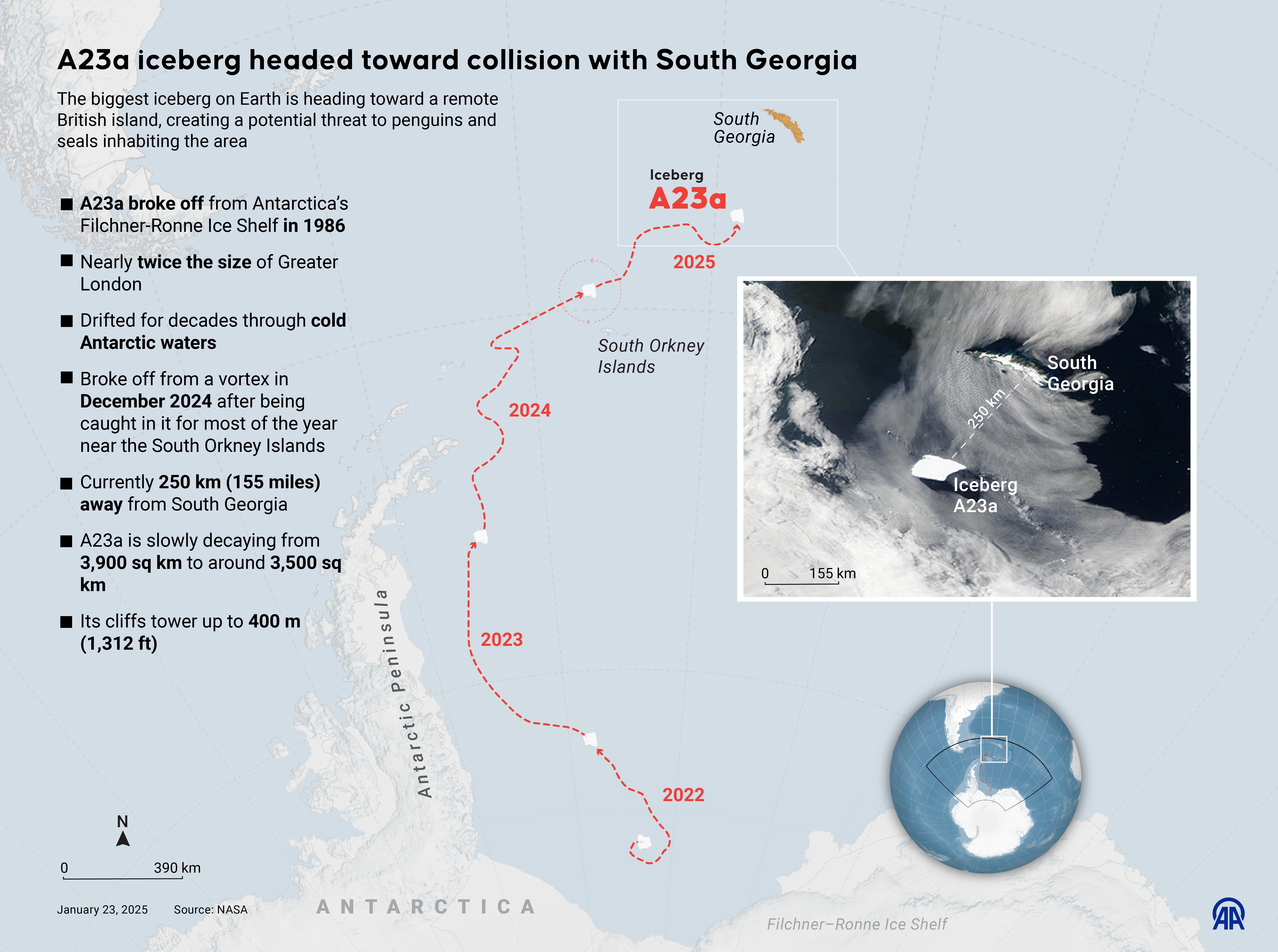
The world’s largest iceberg is on crash course with a remote British island, risking its inhabitants.
The floating giant, compared to Game of Thrones’ ice wall, stretches from horizon to horizon and is heading towards South Georgia Island, a remote Antarctic haven for millions of penguins and seals.
The behemoth, dubbed A23a, poses a potential threat to the island’s delicate ecosystem.
Scientists are monitoring A23a closely, anticipating two possible scenarios: the iceberg could collide with South Georgia and become lodged, or ocean currents might divert it around the island.
If the trillion-ton slab of ice, called a megaberg, gets stuck it could make it hard for penguin parents to feed their babies and some young could even starve.
Overall, however, researchers say they aren’t too worried about major harm from the iceberg.
It’s also a natural process happening more frequently because of human-caused climate change, said British Antarctic Survey physical oceanographer Andrew Meijers, who examined the iceberg up close in December 2023 when it drifted past the research ship RRS Sir David Attenborough.
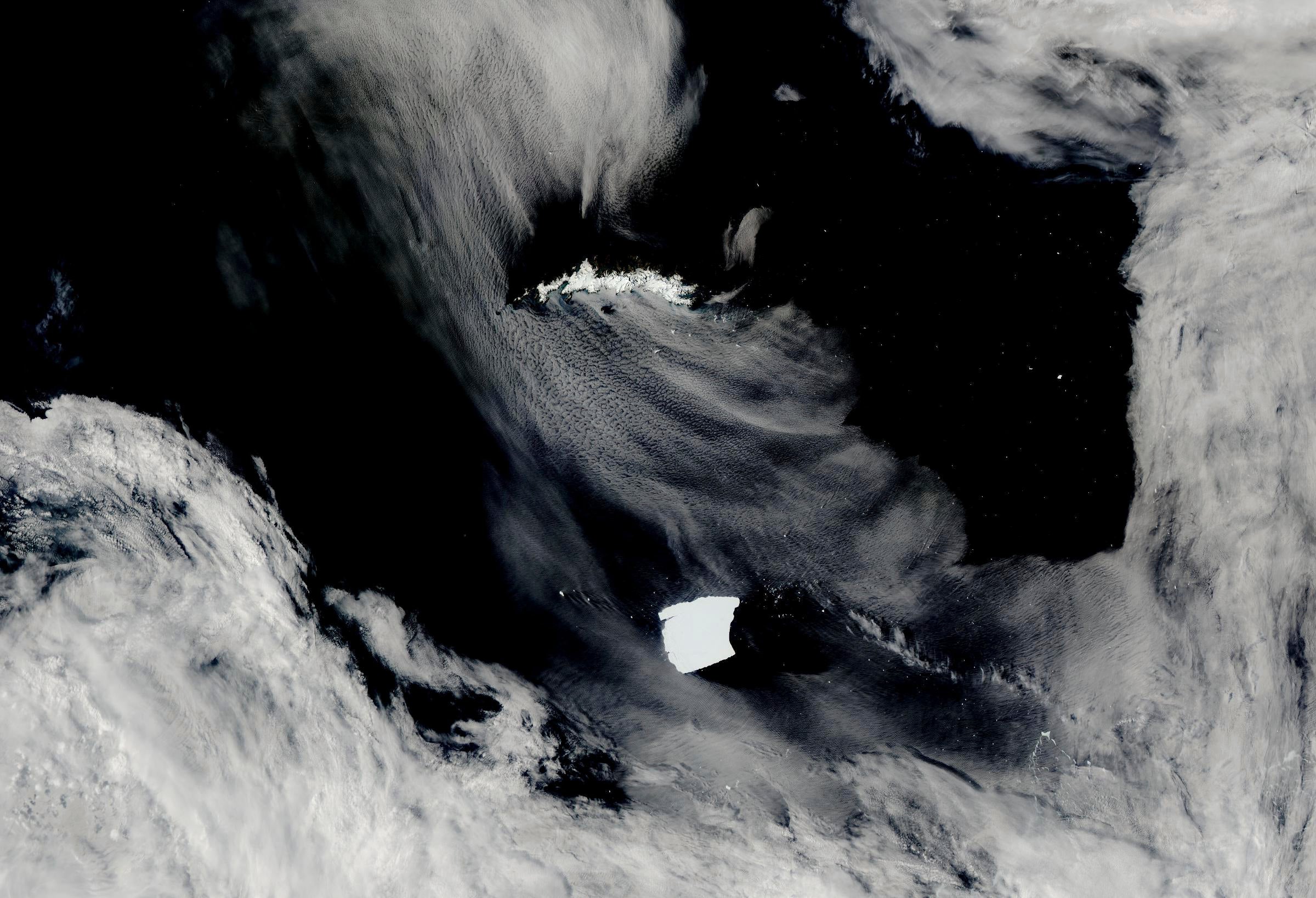
“The iceberg itself is colossal and it stretches from horizon to horizon,” Meijers said Thursday of the 130-foot (40-meter) tall mass. “It’s a huge wall, a Game of Thrones style wall of ice that towers above the ship. With some waves breaking against it and if you get a bit of sunshine coming through, it’s really dramatic.”
For every bit of the iceberg above the water’s surface, there’s ten times more below, Meijers said.
The iceberg is making its way at a glacial pace of one meter every three to seven seconds, much slower than one mile per hour, Meijers said.
In the next two to four weeks the iceberg will approach South Georgia where the water gets shallow, so it could wedge itself in, Meijers said. Or it could slide past.
“Large icebergs bump into the shoals around South Georgia more or less every year — it’s a kind of highway for the major icebergs,” University of Colorado ice scientist Ted Scambos wrote in an email. “This ocean current path has been known since Shackleton’s time, he said, referring to Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton who led British expeditions to the southern continent. Shackleton made the trip to the island in just three weeks. “Usually the icebergs take a bit longer (he had sails),” he said.
A map of South Georgia and Sandwich Islands:
Eventually, this big iceberg will break up into smaller ones and melt as icebergs do, Meijers said.
At full size, it doesn’t represent much of a hazard for fishermen in the area, because they can see it. The bigger concern is penguins which are in their summer breeding cycle, Meijers said.
“South Georgia is an amazingly ecologically rich island. It’s a breeding ground for a huge number of penguins, millions of penguins and seals,” Meijers said. “There’s lots of pups and chicks and they’re all still dependent on their parents.”
The parents go out quite a way into the water and forage. Icebergs can block pathways to their food, making the adults swim farther, burning more energy, bringing back less to the babies. That “unfortunately can dramatically increase mortality rates. And it has happened in the past,” Meijers said.
That’s bad for that colony, but it doesn’t amount to a problem for overall penguin populations, Scambos said.
“The whole ecosystem in the Southern Ocean is very resilient to these events,” he wrote. “It has evolved with these icebergs being a factor for hundreds of thousands of years.”
This iceberg first broke off in 1986 but has been penned in a crowded patch of sea ice for decades until a few years ago, Meijers said.
Calving icebergs are normal, but they are happening more frequently as the climate warms and more fresh water flows into the ocean, Meijers said.

 By The Independent (Science) | Created at 2025-01-24 01:13:29 | Updated at 2025-01-24 10:00:34
12 hours ago
By The Independent (Science) | Created at 2025-01-24 01:13:29 | Updated at 2025-01-24 10:00:34
12 hours ago






