The 2024 election season featured an unprecedented number of Asian Americans, from Vivek Ramaswamy’s rise in the Republican primary to soon-to-be second lady Usha Vance, to the Democratic candidate herself, Kamala Harris. Just a few years ago, this would have been a cause for celebration on the political left: Asian Americans have reliably voted for Democrats for decades. But the election results revealed that racial and ethnic minorities are not as loyal to the Democratic Party as previously believed. Much like Hispanics, Asian American voters made a major shift to the right.
Nationally, 2020 and 2024 exit polls from The Washington Post show a 5-point shift to the Republicans in the presidential race among Asian American voters relative to 2020. In some states, such as Nevada and Texas, the polls suggest that Donald Trump won the Asian American vote outright. The NBC News exit poll found a 5-point shift to the right nationally among Asian Americans relative to 2020. And in their survey of Asian American voters prior to the election, Asian Americans Advancing Justice saw a 7-point shift away from the Democrats relative to 2020.
Exit polls are far from perfect measures of voting behavior, though. A spokesperson for APIAVote, a group that focuses on encouraging Asian American political engagement, pointed out when asked for comment that the exit polls may not be a “representative sample of the Asian American electorate.” For instance, the exit polls were not conducted in any Asian languages, which would preclude some Asian American voters with poor English skills from participating.
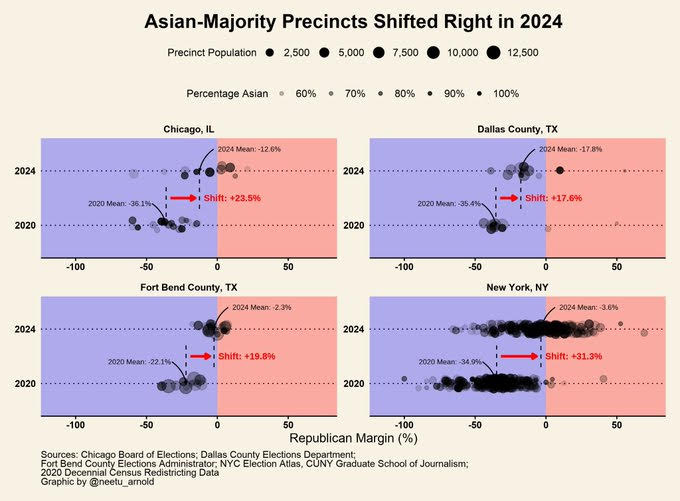
My analysis of precinct-level voting data in four major urban areas shows that the exit polls may actually be understating the degree to which Asian Americans shifted to the right. Using census data, I identified majority-Asian precincts in these areas and compared the Republican margin of victory (or loss) between the 2024 and 2020 elections. The results are much more stark: Majority-Asian precincts in New York City, for instance, saw a rightward shift of 31 percentage points. Precincts in Dallas and Fort Bend counties in Texas both saw rightward shifts between 17 and 20 points. And precincts in Chicago saw a 23-point shift to the right.
If the rightward shift among Asian American voters is real and significant, what is behind it?

 By The Free Press | Created at 2024-11-22 15:55:55 | Updated at 2024-11-22 21:34:45
5 hours ago
By The Free Press | Created at 2024-11-22 15:55:55 | Updated at 2024-11-22 21:34:45
5 hours ago